
Introduction
On the afternoon of Wednesday 6th December 2023, Paul Scriven, a Liberal Democrat peer, introduced his private member’s bill, the Disestablishment of the Church of England Bill, in the House of Lords, after it had been selected by ballot.
In the UK Parliament, the first reading of a bill is usually a mere formality, with the meat of the debate being reserved for the second reading – which may happen a few months later, if there is time and circumstances do not intervene.
When Lord Scriven, however, ‘beg[ged] to introduce a bill to disestablish the Church of England, to make provision for the protection of freedom of religion or belief, and for connected purposes,’ there were noises of dissent halfway through – apparently from the Conservative government’s side.
And when the Lord Speaker, Lord McFall of Alcluith, asked the House whether they were ‘content’ to let the bill be read a first time, there was vociferous opposition, to the point where he initially responded that the ‘not contents’ had it, before changing his mind. The full drama can be seen (and heard) in the video clip linked in Lord Scriven’s tweet below.
A brief history of (dis)establishment
The origin of the establishment of the Church of England was Henry VIII’s Act of Supremacy in 1534. This made him the ‘Supreme Head of the Church of England’ and required that his subjects swear an oath of loyalty recognising his marriage to his second wife, Anne Boleyn, after he had unilaterally decided to cancel his marriage to his first wife, Catherine of Aragon.
The Act of Supremacy was repealed under Henry VIII’s Catholic daughter when she became Mary I, but then re-enacted in 1558 under Elizabeth I. Section VIII, entitled ‘All Spiritual Jurisdiction united to the Crown,’ is still in force today.
The last time a bill was introduced into Parliament that would have disestablished the Church was in 1991, in Tony Benn’s Commonwealth of Britain Bill, which would also have abolished the House of Lords altogether and removed the constitutional role of the monarchy. However, the bill’s second reading was repeatedly deferred and there was never a full debate.
In January 2020, another Liberal Democrat peer, Dick Taverne, introduced a private member’s bill on one aspect of disestablishment: the House of Lords (Removal of Bishops) Bill. This passed its first reading, but fell by the wayside during the pandemic.
Other points in recent history at which disestablishment or the removal of the bishops from the Lords was considered are recorded in a paper on ‘The relationship between church and state in the United Kingdom’, published by the House of Commons Library in September.
The 2018 debate
Disestablishment was briefly debated in the House of Lords on 28 November 2018, under Elizabeth II. A Labour peer, Lord Berkeley, asked the Conservative government ‘what assessment they have made of the case for the disestablishment of the Church of England.’ The laconic answer, from Lord Young of Cookham, was, ‘My Lords, none.’
Lord Berkeley pointed out that attendance at the Church of England was falling rapidly, and that ‘half of British people have no religion’. He therefore proposed that it would be time for Charles, when he became king, ‘to embrace this secular state’ and swear an appropriately non-religious oath. This led to a discussion about the status of the Church of England and constitutional reform.
For anyone who thinks that the bishops in the Lords are a mere relic, their entrenched place in the establishment can be illustrated by a few quotations from this debate. Lord Young argued that the bishops in the Lords ‘add a spiritual dimension to our discussions. They speak with a moral authority that escapes most of us…The bishops seek to heal religious conflict and promote religious tolerance and inclusiveness.’ In a word, the government’s policy was ‘antidisestablishmentarianism’. Without a trace of self-interest, the Lord Bishop of Worcester proposed that ‘the established Church is a significant force for good.’
Lord Scriven’s Bill
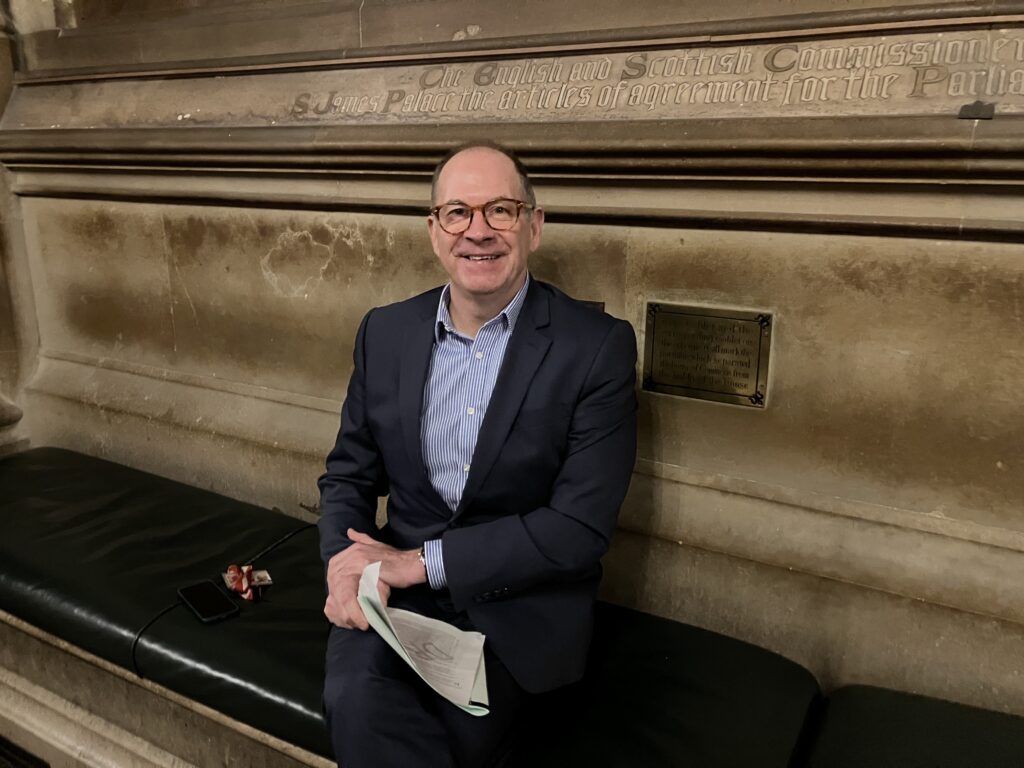
About 24 hours before the Disestablishment Bill was introduced, I interviewed Paul Scriven over a cup of tea in the House of Lords. An edited version of the interview is below. We discuss his motivations for bringing the bill, even though it is almost certainly doomed to fail, and why he is bringing it now, of all times. We also look at the relationship of the Church to the monarchy and of disestablishment to wider constitutional reform; and whether the bishops or other religious leaders really have any claim to moral authority.
~ Emma Park, Editor

Interview
Freethinker: How did you come to introduce this bill?
Paul Scriven: A little bit by accident. I entered the Lords reluctantly, as I do not agree with an unelected second house. In 2014, Nick Clegg wanted to put a number of peers in, like me, who believed that when the time came, we would vote for a reformed elected chamber. I am quite a nonconformist by background. I grew up on a council estate in Huddersfield and have always rallied against authority. When I have seen unfairness, I have fought it. Then Nick finally beat me down and got me into this place. Now that I am here, I realise it is a place where you can champion causes which are important to improve either individual lives or the state of the nation or internationally.
I was an agnostic when I came in. I have sat and watched the Bishops’ Bench for the last nearly ten years, and their views on social matters have made me a confirmed atheist. It is quite clear they are way behind the curve on where the vast majority of Britons are, whether on same-sex marriage or women or a number of issues. If that is Christianity in action from the Church of England perspective, then I do not want anything to do with it. They do not represent modern Britain – that was clear from the 2021 census.
Has being gay influenced your perspective on this issue?
I find some churches’ views on being gay baffling. Others are clearly more progressive. It is hurtful at times having to hear that you are not equal, even though they say that God loves you – and then it is quite clear that they do not like my kind of love. That is wretched. It has not driven me to my position. I just think that, on a wider number of issues, listening to the bishops has made me not want to be associated with what I see as predominantly white old men arguing about how to keep an institution together and very conservative in their views.
I also find it absolutely bewildering that in the UK Parliament, there is only one institution that is guaranteed places, and that is the 26 Anglican bishops who sit in the House of Lords. In 2023, how on earth does a Church which has 0.9% of the population [in England] in regular attendance at a Sunday service have an automatic right to be in Parliament, determine laws and have influence and power beyond its relevance to most people?
More broadly, why is it that the Church of England has so much influence, power and a special status in our society, when those who want to practise any faith or belief should have equality? The time now is ripe for disestablishment – especially when you consider what a diverse country we are, in terms not just of our faith, but of our cultures and beliefs. It seems ridiculous that one religious denomination should have a special status that goes back to a king wanting a divorce in the 1500s.
In terms of tactics, the next general election has to take place no later than January 2025. Did you ever consider leaving the bill until the next government?
Very few private member’s bills actually become law. In all honesty, I think it is more likely that snow will fall in hell than that my bill will get through this time. It is important, though, to raise the issue, because of the diversity of beliefs and faiths revealed by the 2021 census. I could stay quiet and hope for the next government to have a different view, which I think highly unlikely. It will have a large legislative programme and probably the disestablishment of the Church of England will not be among its priorities.
If the bill falls, I can file it again at the start of the next Parliament. I am looking at this in the longer term. During the debate in the second reading, I will be able to listen to people’s objections and amend the bill, which will hopefully strengthen it next time round.
Is the bill officially supported by the Liberal Democrats?
No, as a private member’s bill it is not. It is not an issue which I discussed with my party first. I am sure that as the debate happens and as the bill progresses, there will be cross-party support from all over the House. My guess is that there will also be opposition from people of different parties too.
How did the drafting process work?
I had been in touch with the National Secular Society (NSS) over a number of issues, and I just said to them, I think now is the time to introduce the private member’s bill for disestablishment. We had a discussion and they told me what was important to them. I also had discussions with Humanists UK (HUK). There were a number of issues which both organisations wanted in the bill. To actually draft the bill in appropriate parliamentary language, I worked with the House of Lords Private Bill Office.
Apart from the NSS and HUK, did you work with any other organisations on the bill?
Those were the two organisations that reached out and spoke to me. I have had quite a lot of emails from people in the Church of England supporting disestablishment. They have told me that, for them, there is a real feeling that disestablishment could be liberating. They would no longer be seen as an organ of the state, and would be able to start doing things based on their true mission, which were not either weakened or diluted by their Church’s established status.
Have you asked the bishops for their point of view?
I talked to the Bishop of Sheffield briefly about it. They will probably disagree. And when we get to the second reading, they will have arguments as to why they want to keep their privileged status and their seats in Parliament. However, they do not come from a position of neutrality. It will be interesting to see if they all have the same view.
Is your argument for disestablishment premised on the state of the Church of England now, or is it a matter of principle, or both?
It is a matter of principle. No faith or belief should have a special status. People should be able to pursue their belief or religion equally.
One possibility sometimes mooted by supporters of religion is that, instead of simply having 26 bishops, the major religions and Christian denominations in the UK could all have allocated seats. What would you say to this?
Religions do not have a monopoly on morals, they do not have a monopoly on insight. You only have to look at some of the child abuse scandals in the Church of England and how they were covered up to realise that. If an individual within a church or a belief system has such significant impact that they can help influence the House of Lords in its present form, then they should by all means be individually nominated. But it should not be the very fact that they are an office-holder or attached to a particular religion.
One common view about the bishops in the Lords is that, well, they are quite nice, and are probably overall a good rather than a bad influence on legislation. How would you respond to that?
They are an influence. It is not for me to determine whether they are good or bad. They have a vested interest to ensure that they can use this place to ingrain their privileged position. On a number of occasions, I have been on the same side of the argument as the bishops, such as in the Illegal Migration Bill. But the fact that they are bishops does not mean that they should automatically be here and able to make those points.
Is there an analogy between bishops and hereditary peers, in terms of their lack of democratic legitimacy?
Being a hereditary peer depends on which womb you came out of. But even the hereditary peers in the Lords are now elected before they get here, unlike the bishops, who are plonked in because of the church they are in.
The peers are chosen by the world’s smallest electorate…
Yes. But the bishops come because they decided to study a certain theological doctrine and then they have climbed the greasy pole within a particular church. It is very odd to me.
What about the technicalities of disestablishment? I have heard some Anglicans saying that they support disestablishment in theory, but in practice it would simply be too difficult to disentangle all the knots that bind Church and State.
Isn’t that interesting? What they are really doing is arguing that they have got their fingers and their claws in so many parts of our constitution that it would be too difficult to touch it. On that argument, quite a lot of legislation would never get done.
My bill is not specific about the technicalities. It asks that, within six months of its being passed, a committee is set up for a year to look at the legal implications of what needs to happen to disestablish the Church of England. The committee would be made up of relevant legal practitioners and people who are specialists in the constitution and in law to do with the Church of England. A report then goes to the Secretary of State, and within six months of receiving that report, the Secretary of State has to produce a detailed legal bill on disestablishment. I am not saying this is going to be easy. There are going to be some very difficult conundrums in there, for example over the Act of Union.
Difficulty should not be a reason for not legislating, but for doing it carefully, with good legal minds and an appropriate timescale.
In terms of the implications of disestablishment, the Church of England owns a lot of property. What do you say should happen to it?
I do not want to get into a big argument about this. My bill says that property will go to the Church’s General Synod. And the sovereign will no longer have the title ‘Defender of the Faith’.
Talking of the monarchy, is getting rid of it a logical next step after disestablishment?
No, that does not automatically follow. There are many functioning constitutional monarchies in Europe where the monarch is not head of the church. So one does not follow from the other. Personally, I am not a republican. I believe in a European-style constitutional monarchy.
What sort of a coronation would you envisage post-disestablishment?
A non-religious one, which would crown the monarch as the constitutional monarch of the country, not as the head of a particular faith. It could be quite interesting to develop a new coronation.
Presumably the monarch would no longer be obliged to be Anglican?
Yes. This is not rocket science. Religion would come out of the coronation, and the monarch would no longer be the ultimate boss of the Church of England.
What about other religions with a presence in Parliament? As things stand, do they have much influence behind the scenes?
Not as much as the established church. There are people of faith – Christian, Muslim, Sikh – or of no faith, like the Humanists, who try to exert influence on legislation. But the difference is that it is equal and they have to win the argument. They have not got an ingrained position. I would not want to stop that. One of the purposes of my bill is to defend people’s right to have faith and non-belief, and to be able to pursue that equally.
One of the arguments that will get thrown about is that I am anti-religious. What I actually want to do is level the playing field between the influence of all faiths and beliefs.
Taking a step back, how far are we from full-scale House of Lords reform?
It is going to be a long journey. At the age of 48, I came here naïvely thinking I would be a turkey voting for Christmas. I am now 57, and I have worked out since being here that the evolution of the British system is not always as fast as you want it to be. To reform the House of Lords would take a lot of effort and heartache. I do not think Labour will do it in their first term, but if they get in for a second term, then there may be some significant reform. My guess is that it will be in steps rather than a big leap, which is the way that the British have tended to go for their revolutions for many centuries now. The removal of the hereditary peers and the bishops might be one of the first possible reforms in terms of moving to a democratically elected chamber eventually. Other reforms might include lowering the size of the House, fixing a retirement age for peers, and changing the way that peers are selected.
As you say, disestablishment may not be high on a Labour government’s list of reforms. Indeed, why should it be high on anyone’s agenda, when we have so many other problems in the UK to deal with?
Things that affect people’s lives every day, such as the health service, the economy, housing, safety, are always going to be there. I am not suggesting for one moment that the disestablishment of the Church of England should take priority over the health service, for instance. What my bill intends to do is to raise awareness so that when the time is right and government space becomes available, there will be public understanding and the pressure to deliver disestablishment. Eventually, the public will say, ‘Now is the time for change.’
And when will ‘eventually’ be?
I cannot give you an answer. We are getting the ball rolling; maybe it will happen in my lifetime, maybe it won’t. But we shall keep pushing for it. And hopefully it will become such a public discussion that, one day, the government will make time for it.








1 comment
“One possibility sometimes mooted by supporters of religion is that, instead of simply having 26 bishops, the major religions and Christian denominations in the UK could all have allocated seats. What would you say to this?”
Whenever I hear this argument I always think, but who decides what the major religions are? Why just those religions? Why are other religions being ignored? What is the threshold for being considered a major religion? Who would be checking any claims for numbers of followers?
There are so many questions that would have to be answered that the only sensible response is that no religion should be allowed any special privileges.
Your email address will not be published. Comments are subject to our Community Guidelines. Required fields are marked *
Donate